

 “Advance Australia Fair”
“Advance Australia Fair”


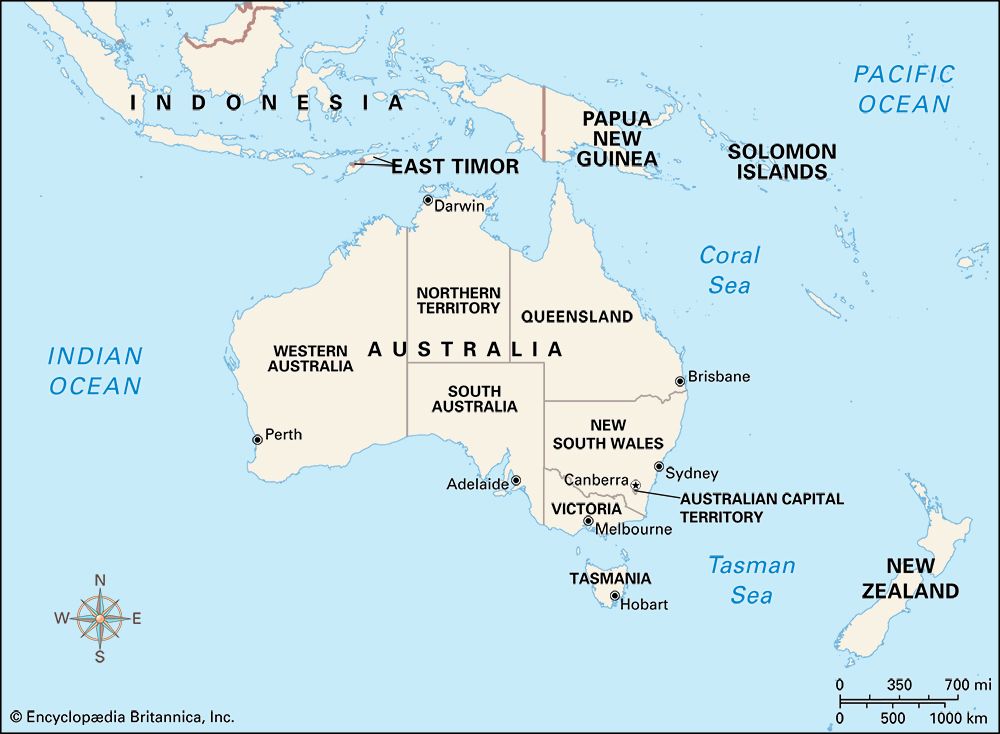
 Australia is one of the largest countries in the world, but it is also the smallest continent. Located south of Asia, Australia lies between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. Off the southeastern coast is the island of Tasmania. Along the northeastern coast is the world’s largest coral reef, the Great Barrier Reef.
Australia is one of the largest countries in the world, but it is also the smallest continent. Located south of Asia, Australia lies between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. Off the southeastern coast is the island of Tasmania. Along the northeastern coast is the world’s largest coral reef, the Great Barrier Reef.- Bodies of water: the seas and straits of the Indian Ocean and Pacific Ocean include Tasman Sea, Timor Sea, Arafura Sea, Gulf of Carpentaria, Torres Strait, Coral Sea
- Interior: the Outback, or the “bush,” is a vast, dry area where few people live
- Deserts: Great Victoria Desert, Great Sandy Desert
- Mountains: Great Dividing Range on the east coast; Australian Alps in the southeast
- Highest point: Mount Kosciuszko—7,310 feet (2,228 meters)
- Major rivers: Darling, Murray
- Major cities: Sydney, Brisbane, Melbourne, Perth, Canberra
 Australia is very dry. Most areas have hot summers and mild winters. Because Australia is in the Southern Hemisphere, summer starts in December, and winter starts in June.
Australia is very dry. Most areas have hot summers and mild winters. Because Australia is in the Southern Hemisphere, summer starts in December, and winter starts in June.
 Australia has been a separate land mass for millions of years, so it has many species, or kinds, of plants and animals that are not found anywhere else on Earth. Australia’s plants vary from region to region. The rainforests of the northeast include flowering plants, palms, and laurels. Woodlands and forests cover eastern Australia. Eucalyptus trees are common in the highlands of the south and at the edges of the deserts. Desert shrubs and grasses grow in dry areas.
Australia has been a separate land mass for millions of years, so it has many species, or kinds, of plants and animals that are not found anywhere else on Earth. Australia’s plants vary from region to region. The rainforests of the northeast include flowering plants, palms, and laurels. Woodlands and forests cover eastern Australia. Eucalyptus trees are common in the highlands of the south and at the edges of the deserts. Desert shrubs and grasses grow in dry areas.




More than 90 percent of Australians have European roots. The first settlers on the continent were white people from Europe. They did not welcome other groups. In 1901, when Australia became an independent country, it made racial discrimination an official policy. It said that non-white immigrants could not enter the country. The policy did not change until 1973. Since then, many Asians have immigrated to the continent.
 A small percentage of the population is made up of Torres Strait Islander peoples and Aboriginal peoples. Aboriginal Australians had lived on the continent for more than 50,000 years before the Europeans arrived in about 1788. Historians estimate that at that time there were at least 300,000 Indigenous Australians. However, European contact and colonization were deadly for the Indigenous peoples. Their population was reduced by as much as 90 percent. Until very recently, laws limited the rights and actions of Indigenous Australians. Such laws have changed, but the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples do not agree with the government on all issues.
A small percentage of the population is made up of Torres Strait Islander peoples and Aboriginal peoples. Aboriginal Australians had lived on the continent for more than 50,000 years before the Europeans arrived in about 1788. Historians estimate that at that time there were at least 300,000 Indigenous Australians. However, European contact and colonization were deadly for the Indigenous peoples. Their population was reduced by as much as 90 percent. Until very recently, laws limited the rights and actions of Indigenous Australians. Such laws have changed, but the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples do not agree with the government on all issues.
Almost 44 percent of Australians are Christians. The next biggest religious groups are Muslims, Hindus, and Buddhists. A little less than 40 percent of the population do not follow any religion.




 Few people live in the Outback. A little more than 90 percent of all Australians live in cities, mostly along the coasts. Five major cities have a population of more than one million: Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, and Adelaide.
Few people live in the Outback. A little more than 90 percent of all Australians live in cities, mostly along the coasts. Five major cities have a population of more than one million: Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, and Adelaide.

 Australian culture is a mixture of Aboriginal, European, and Asian influences. Whatever their heritage, Australians are known for their love of the outdoors. Australians often visit their local beaches, where they surf, kayak, fish, or spend time with friends. It’s common to take trips into the Outback to experience the nature there as well. Another popular outdoor tradition, especially in warmer weather, is the barbecue, or “barbie.” The barbie is a casual gathering of friends and family. Everyone brings food, and some of it is grilled on the barbie. Although Australian food is not popular worldwide, many Australians are dedicated to Vegemite, a paste that is high in nutrition. It is used as a spread on toast, as a pasta topping, and as a glaze for meats.
Australian culture is a mixture of Aboriginal, European, and Asian influences. Whatever their heritage, Australians are known for their love of the outdoors. Australians often visit their local beaches, where they surf, kayak, fish, or spend time with friends. It’s common to take trips into the Outback to experience the nature there as well. Another popular outdoor tradition, especially in warmer weather, is the barbecue, or “barbie.” The barbie is a casual gathering of friends and family. Everyone brings food, and some of it is grilled on the barbie. Although Australian food is not popular worldwide, many Australians are dedicated to Vegemite, a paste that is high in nutrition. It is used as a spread on toast, as a pasta topping, and as a glaze for meats.

 Australia is home to a large sports culture. Football (soccer), rugby, cricket, and Australian rules football are some of the most popular sports to play and to watch. Australian athletes have been successful in international sporting competitions. Australia has won more Olympic swimming medals than any other country except for the United States. Australia has the most successful men’s national cricket team in the world. The team has won the Cricket World Cup six times. The Australian women’s netball team is also the most successful in the world. It has won 12 Netball World Cup titles.
Australia is home to a large sports culture. Football (soccer), rugby, cricket, and Australian rules football are some of the most popular sports to play and to watch. Australian athletes have been successful in international sporting competitions. Australia has won more Olympic swimming medals than any other country except for the United States. Australia has the most successful men’s national cricket team in the world. The team has won the Cricket World Cup six times. The Australian women’s netball team is also the most successful in the world. It has won 12 Netball World Cup titles.
Art is an important part of Australian Aboriginal culture. The oldest rock art in Australia can be traced back more than 17,000 years ago in the Kimberley region of Australia. Today artists paint on canvas, eucalyptus bark, and leaves and sculpt and carve their works of art. All Aboriginal art, in the past and now, is connected to stories of the Dreaming. The Dreaming is the Aboriginal peoples’ understanding of how the world and life was created by ancestor spirits.


 Australia is one of the wealthiest countries in the world. All areas of its economy are strong. Most people work in services.
Australia is one of the wealthiest countries in the world. All areas of its economy are strong. Most people work in services.
- Agriculture: Livestock is the largest part of the agriculture sector. Cattle is the most important animal, followed by sheep and poultry. Australia is one of the world’s largest producers of wool. The wool comes from more than 60 million sheep. For crops, Australia is usually in the top five for wheat production. Other important crops include barley, canola, potatoes, fruits, nuts, and cotton.
- Mining: Australia’s rich natural resources include oil, coal, and natural gas. The country is a leading world producer of iron ore, coal, bauxite, copper, and aluminum. Australia contains about 95 percent of the world’s opal deposits.
- Manufacturing: Australian factories make food and beverages, machinery, metal products, chemicals, textiles, and more.
- Services: The largest section of the Australian economy is services. This includes a wide range of activities, such as finance and insurance, education, health care, publishing, tourism, and entertainment.
| name | party | term |
|---|---|---|
| Edmund Barton | 1901–03 | |
| Alfred Deakin (1st time) | Liberal-Labor | 1903–04 |
| John Christian Watson | Labor | 1904 |
| George Houston Reid | 1904–05 | |
| Alfred Deakin (2nd time) | Liberal-Labor | 1905–08 |
| Andrew Fisher (1st time) | Labor | 1908–09 |
| Alfred Deakin (3rd time) | Liberal-Conservative | 1909–10 |
| Andrew Fisher (2nd time) | Labor | 1910–13 |
| Joseph Cook | Liberal | 1913–14 |
| Andrew Fisher (3rd time) | Labor | 1914–15 |
| William Morris Hughes (1st time) | Labor | 1915–16 |
| William Morris Hughes (2nd time) | Nationalist | 1916–23 |
| Stanley Melbourne Bruce | Nationalist-Country | 1923–29 |
| James Henry Scullin | Labor | 1929–32 |
| Joseph Aloysius Lyons | United Australia | 1932–39 |
| Earle Page | Country–United Australia | 1939 |
| Robert Gordon Menzies (1st time) | United Australia | 1939–40 |
| Robert Gordon Menzies (2nd time) | United Australia–Country | 1940–41 |
| Arthur William Fadden | Country–United Australia | 1941 |
| John Curtin | Labor | 1941–45 |
| Francis Michael Forde | Labor | 1945 |
| Joseph Benedict Chifley | Labor | 1945–49 |
| Robert Gordon Menzies (3rd time) | Liberal-Country | 1949–66 |
| Harold Holt | Liberal-Country | 1966–67 |
| John McEwen | Liberal-Country | 1967–68 |
| John Grey Gorton | Liberal-Country | 1968–71 |
| William McMahon | Liberal-Country | 1971–72 |
| Gough Whitlam | Labor | 1972–75 |
| Malcolm Fraser | Liberal–National Country | 1975–83 |
| Robert Hawke | Labor | 1983–91 |
| Paul Keating | Labor | 1991–96 |
| John Howard | Liberal-National | 1996–2007 |
| Kevin Rudd (1st time) | Labor | 2007–10 |
| Julia Gillard | Labor | 2010–13 |
| Kevin Rudd (2nd time) | Labor | 2013 |
| Tony Abbott | Liberal-National | 2013–15 |
| Malcolm Turnbull | Liberal-National | 2015–18 |
| Scott Morrison | Liberal-National | 2018–22 |
| Anthony Albanese | Labor | 2022– |
Federal Government
 The British monarch is the formal head of state, but the power of the monarch is limited by the government. The British monarch lives in Great Britain and is usually not in Australia. Therefore, the monarch is represented by a governor-general. The governor-general is not an elected official. He or she is appointed to the position.
The British monarch is the formal head of state, but the power of the monarch is limited by the government. The British monarch lives in Great Britain and is usually not in Australia. Therefore, the monarch is represented by a governor-general. The governor-general is not an elected official. He or she is appointed to the position.
The Australian constitution divides the government into three branches: the legislative, the executive, and the judicial. As in the British government, Australia’s legislature is a parliament. The Australian Parliament consists of two houses: the House of Representatives and the Senate. Parliament writes and passes laws.
The executive branch enforces the laws. It is headed by the prime minister. The prime minister is a member of Parliament and the leader of the party with the most seats in Parliament. The prime minister works with a group of people called ministers. Together they are responsible for all the government’s policies and decisions.
The judicial branch interprets the laws made by Parliament. The branch is made up of a system of federal courts. The High Court of Australia is the highest court in the country.
State and Local Governments
In Australia the states have the power to make their own laws over matters not controlled by the federal government. The federal government is responsible for taxation, defense, foreign policy, immigration, customs, the post office, and broadcasting. Each state has its own constitution and its own structure of legislative, executive, and judicial branches. The head of each state government is called the premier, and the British monarch is represented by a governor. Within each of the six states, as well as the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory, there are local communities with their own governments. These local communities include cities, towns, villages, and shires.


 Aboriginal peoples lived in Australia for more than 50,000 years before Europeans arrived. They came from Asia by boat or by land that is now underwater. Aboriginal peoples lived in groups that had their own language, culture, and traditional lands. These lands, known as Country, were central to the survival of each group. The people knew how to protect and use the environment of their specific Country. This is what Europeans encountered when they first landed on Australia.
Aboriginal peoples lived in Australia for more than 50,000 years before Europeans arrived. They came from Asia by boat or by land that is now underwater. Aboriginal peoples lived in groups that had their own language, culture, and traditional lands. These lands, known as Country, were central to the survival of each group. The people knew how to protect and use the environment of their specific Country. This is what Europeans encountered when they first landed on Australia.
Portuguese and Spanish explorers may have landed in Australia in the 1500s. In the 1600s several Dutch explorers reached the continent. They included Dirck Hartog and Abel Tasman. Hartog discovered the west coast, and Tasman sailed along the southern tip of what is now called Tasmania. Because of all these voyages, the Dutch named the continent New Holland in 1644. But they did not settle there.
 William Dampier, an English pirate turned explorer, landed on the west coast twice in the late 1600s. In 1770 Captain James Cook landed in southeastern Australia and claimed it for Great Britain. He named the region New South Wales. Others later explored the continent further, including Matthew Flinders, who suggested the name Australia.
William Dampier, an English pirate turned explorer, landed on the west coast twice in the late 1600s. In 1770 Captain James Cook landed in southeastern Australia and claimed it for Great Britain. He named the region New South Wales. Others later explored the continent further, including Matthew Flinders, who suggested the name Australia.
First Fleet and Settlement
 Captain Cook thought that New South Wales was a good place for settlement. At the time, England’s prisons were overcrowded. So the English government decided to send prisoners to Australia to start a penal colony—a place where criminals are sent to live.
Captain Cook thought that New South Wales was a good place for settlement. At the time, England’s prisons were overcrowded. So the English government decided to send prisoners to Australia to start a penal colony—a place where criminals are sent to live.
Captain Arthur Phillip was in charge of the First Fleet. He led 11 ships carrying about 200 marines, a few free settlers, more than 700 convicts, food stores, and farm animals. The trip took eight months and conditions were very hard. They reached Australia in January 1788 and settled in a bay that they named Sydney Cove. Phillip became the first governor of the colony.
 Convicts and settlers worked to clear land and to establish farms. They were not used to the climate, which was different from England, so the colonists struggled to survive. But soon more convicts and settlers arrived. The settlement grew bigger and stronger. In the 1800s other parts of the country were settled. Some were also penal colonies. In 1851 the discovery of gold drew thousands of new immigrants to Australia. The settlements grew and became colonies separate from New South Wales. They became Tasmania, Western Australia, Victoria, Queensland, and South Australia.
Convicts and settlers worked to clear land and to establish farms. They were not used to the climate, which was different from England, so the colonists struggled to survive. But soon more convicts and settlers arrived. The settlement grew bigger and stronger. In the 1800s other parts of the country were settled. Some were also penal colonies. In 1851 the discovery of gold drew thousands of new immigrants to Australia. The settlements grew and became colonies separate from New South Wales. They became Tasmania, Western Australia, Victoria, Queensland, and South Australia.
The flood of settlers nearly wiped out the Aboriginal population. Many Aboriginal people died while fighting for their land or from European diseases.
Independence and War
By the late 1800s the six separate colonies each had an elected assembly. In 1901 they became states when they joined together to form a federation. The new Commonwealth of Australia had a national parliament and six state parliaments. It kept ties with Britain, however, as part of the British Commonwealth (a group of former British colonies).
 When World War I began, Australians fought alongside the British Army. Many Australians died during the Battle of Gallipoli in 1915. Australia also supported Britain when World War II began in 1939. In the 1940s the Japanese attacked several Australian cities. Their airplanes bombed Darwin, and submarines fired on Sydney. After the war Australia’s population grew rapidly. Many immigrants came from war-torn Europe.
When World War I began, Australians fought alongside the British Army. Many Australians died during the Battle of Gallipoli in 1915. Australia also supported Britain when World War II began in 1939. In the 1940s the Japanese attacked several Australian cities. Their airplanes bombed Darwin, and submarines fired on Sydney. After the war Australia’s population grew rapidly. Many immigrants came from war-torn Europe.
Recent Events
In the 1970s Australia started to focus less on Europe and more on its Asian neighbors. Many Asian immigrants arrived, and trade increased between Australia and Asian countries.
In the 1990s Indigenous Australians won some rights to land. They also won more respect from white Australians. Many still face hardships, however. In 2008 the country’s prime minister issued a formal apology to Aboriginal Australians for abuses they suffered under earlier Australian administrations.
The British monarch is still the head of state in Australia. Some Australians have called for change. They want the country to become a republic with a president as head of state. In 1999, however, Australians voted against a complete separation from Britain.
 The main political parties in Australia are the Australian Labor Party, the Liberal Party of Australia, and the National Party. The Liberal and National parties shared power for much of the second half of the 1900s. In 2007 the Labor Party was elected with Kevin Rudd as prime minister. Three years later Julia Gillard took over as leader of the Labor Party. She therefore became the country’s first woman prime minister.
The main political parties in Australia are the Australian Labor Party, the Liberal Party of Australia, and the National Party. The Liberal and National parties shared power for much of the second half of the 1900s. In 2007 the Labor Party was elected with Kevin Rudd as prime minister. Three years later Julia Gillard took over as leader of the Labor Party. She therefore became the country’s first woman prime minister.
Shortly after taking office, Gillard called for a new election, which took place in late August 2010. The results were extremely close. Neither Labor nor the Liberals won a majority in the House of Representatives. Several independent members of Parliament eventually agreed to support the Labor Party. This allowed Gillard to form a minority government in early September. In 2013, however, the members of the Labor Party voted to replace her as leader of the party. Rudd once again became the leader of the party and the prime minister.
Less than three months later, the Labor Party lost the next general election. A coalition of the National and Liberal parties, led by Tony Abbott, won the election. Rudd stepped down as leader of the Labor Party, although he kept his seat in Parliament. In 2015 Malcolm Turnbull challenged Abbott for the Liberal Party leadership. Turnbull won and became prime minister. He resigned in 2018. Scott Morrison was then elected the new leader of the Liberal Party and became prime minister.
 Australia suffered several major natural disasters in the early 2000s. In early 2009 a series of bushfires killed 173 people, injured 500, and destroyed numerous homes in the state of Victoria. Almost two years later torrential rains caused massive flooding in Queensland and other states. In late 2019 and early 2020 the country faced another series of devastating bushfires. In 2021 and 2022 eastern Australia was once again devastated by flooding.
Australia suffered several major natural disasters in the early 2000s. In early 2009 a series of bushfires killed 173 people, injured 500, and destroyed numerous homes in the state of Victoria. Almost two years later torrential rains caused massive flooding in Queensland and other states. In late 2019 and early 2020 the country faced another series of devastating bushfires. In 2021 and 2022 eastern Australia was once again devastated by flooding.
Morrison and his party were partly blamed for the bushfires and floods that occurred during his term in office. Many people thought that climate change led to the disasters and that Morrison did not do enough to combat climate change. In 2022 Morrison and the Liberal Party were voted out of office. Anthony Albanese became the new prime minister. He faced continuing problems with climate change and with the disease known as COVID-19. The disease, caused by a coronavirus, had killed more than 8,000 people since the beginning of the outbreak in 2020.




